Ever wondered how those delicious pistachios grow? From the lush orchards and botanic gardens to your snack bowl, the journey of these delectable nuts, seeds, and tree crops is nothing short of fascinating. Let’s delve into the captivating process and uncover the secrets behind this green-hued delight of leaves. Curious about what makes pistachios so unique? Join us as we explore their growth cycle, from planting seeds to harvest, and unravel the intricate stages that contribute to their irresistible flavor and crunch. Get ready for an eye-opening adventure through the world of pistachio cultivation, planting seeds and dealing with pest.

Understanding Pistachio Trees
Native Regions
Pistachio trees, belonging to the cashew family, are native to regions in Central Asia and the Middle East. These small, deciduous nut trees thrive in arid climates with long, hot summers and cool winters. The tree’s ability to withstand harsh conditions and pest makes it well-suited for growth in these regions.
The dry climate and zone of these areas are ideal for pistachio cultivation as it helps prevent diseases that can harm the trees. The variation between hot summers and cold winters is crucial for proper fruit development. This natural habitat provides an optimal environment for pistachios, seeds, and pollinator posts to grow and flourish.
Fruit Production
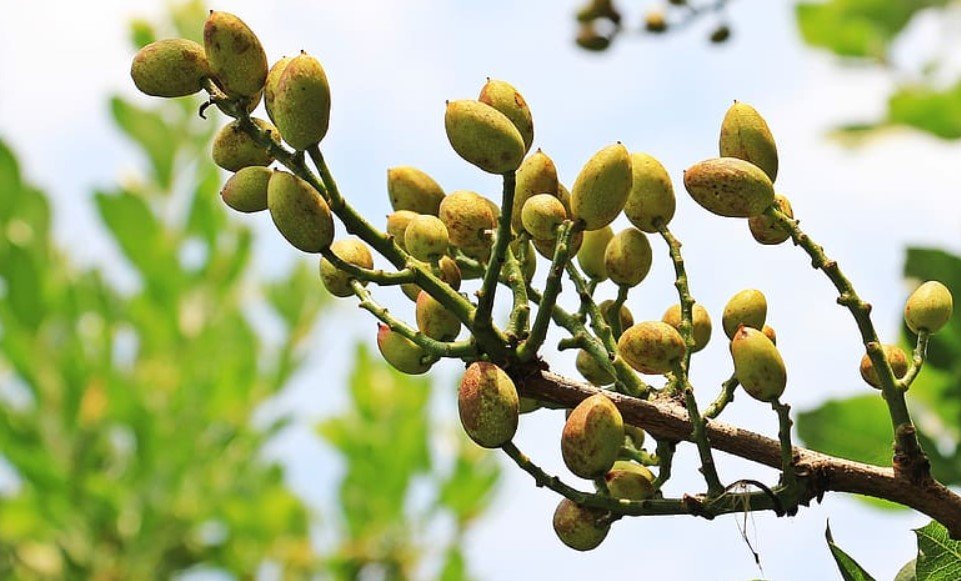
Pistachio trees produce clusters of drupe fruits that contain edible pistachio nuts. The process begins with the appearance of small clusters of flowers on the tree during springtime. These flowers are either male or female; however, not all varieties require cross-pollination for fruit production.
After successful pollination, which can be facilitated by wind or insects, these flowers develop into drupe fruits containing a single seed – this seed is what we know as a pistachio nut. Over time, these nuts mature within their shells until they are ready for harvesting.
Harvesting typically occurs during late summer when the outer hulls split open naturally due to changes in humidity levels. Once harvested from the tree, pistachios undergo processing to remove any remaining hull residue before being packaged and distributed worldwide.
Ideal Growing Conditions for Pistachios
Hot, Dry Climates
Pistachio trees thrive in dry climates with long, hot summers and mild winters. This climate is essential for the optimal growth and development of pistachios. The dry climate helps to prevent diseases that can arise from excessive moisture, ensuring the health and productivity of the trees. In high humidity regions, pistachio trees are more susceptible to fungal diseases and may not yield a good harvest.
The lack of rainfall in arid climates also prevents issues such as root rot, which can be detrimental to the health of pistachio trees. Without excess moisture lingering in the soil, these trees at the location have a greater chance of flourishing and producing high-quality nuts.
Well-Drained Soil
In addition to climatic conditions, soil plays a crucial role in successful pistachio cultivation. Pistachio trees require well-drained soil and a suitable location to prevent waterlogging around their roots. Excessive moisture around the roots can lead to root rot and other water-related problems that hinder tree growth.
Well-drained soil allows oxygen to reach the roots while preventing them from sitting in standing water. This promotes healthy root development and overall tree vigor. It’s important for farmers or growers looking into cultivating pistachios to ensure that their chosen location has suitable soil drainage before planting these valuable nut-bearing trees.
Full Sun Exposure
For optimal growth and nut production, pistachio trees need full sun exposure throughout the day. Adequate sunlight is vital for photosynthesis—the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy—and overall tree vitality.
Without sufficient sunlight, pistachio trees may struggle to produce an abundant crop of nuts or may exhibit stunted growth due to insufficient energy production through photosynthesis.
The Life Cycle of a Pistachio Tree
Maturation Process
Pistachio trees are known for their long lifespan, taking approximately 7-10 years to reach maturity. During this time, the tree undergoes various stages of growth and development. It starts as a small sapling, gradually growing into a mature tree capable of producing fruits.
The maturation process is crucial for pistachio trees as it directly impacts their ability to bear fruit. Proper care and attention during this period can significantly influence the overall health and productivity of the tree.
Annual Cycles
Pistachio trees follow annual cycles that include periods of dormancy, flowering, fruit development, and harvesting. These cycles play an integral role in the continuous production of pistachios year after year.
Dormancy allows the tree to conserve energy during harsh weather conditions or unfavorable environments. When spring arrives, the tree transitions into its flowering stage, where it produces delicate clusters of flowers that eventually develop into pistachio nuts. This phase marks a critical stage in the life cycle as it sets the foundation for future harvests.
Proper care and maintenance are vital throughout these annual cycles to ensure optimal growth and fruit production. Factors such as adequate water supply, nutrient-rich soil, and protection from pests contribute to sustaining healthy annual cycles for pistachio trees.
Pollination Process in Pistachio Cultivation
Dioecious Nature
Pistachio trees are dioecious, meaning they have separate male and female trees. This means that a single tree cannot self-pollinate, requiring the presence of both male and female trees for successful reproduction. Without this unique characteristic, pistachios would not be able to produce nuts.
The male trees produce pollen, while the female trees bear the fruit (pistachio nuts). The separation of sexes is crucial for effective pollination and nut production in pistachio cultivation.
Cross-Pollination Importance
For fruit set and nut production to occur in pistachio orchards, cross-pollination between the male and female trees is essential. Bees are commonly used as natural pollinators, transferring pollen from the male flowers to the receptive stigma of the female flowers. This process allows for fertilization and subsequent development of pistachio nuts.
Growers often strategically place bee colonies near their orchards during bloom time to ensure adequate pollination. Some growers may also use specialized techniques such as applying specific fertilizers or planting certain types of cover crops that attract beneficial insects like bees. These practices help enhance pollination efficiency within pistachio orchards.
From Flowering to Fruit Development
Early Spring Flowering
Pistachio trees start their flowering stage in early spring when the weather gets warmer. This is a crucial time for the trees as they prepare to produce fruits. The pistachio tree’s flowers play a vital role in this process, as successful pollination leads to the development of small green fruits known as drupes.
The warming weather signals the beginning of the flowering stage for pistachio trees. During this time, male and female flowers appear on separate trees. The male flowers release pollen, which is then carried by wind or insects to reach the female flowers on other trees, leading to fertilization and fruit formation.
After successful pollination, these tiny green drupes begin their journey towards becoming fully matured pistachios that are ready for harvest.
Maturation Process
As these small green drupes develop further, they undergo an intriguing transformation. Initially appearing in shades of vibrant green, these developing fruits gradually transition into a striking red hue before eventually maturing into a distinctive beige color.
This maturation process is visually captivating and indicative of the progress made by each individual pistachio fruit from its initial stages as tiny drupes through to full maturity.
The changing colors signify that nature’s course is taking place – signaling that soon enough, these once-green fruits will be ripe and ready for harvesting.
Harvesting Pistachios
Late Summer or Early Fall
Pistachios are typically harvested in late summer or early fall, after the fruit has fully developed. The timing is crucial to ensure that the nuts have matured and are ready for harvest. This period marks the culmination of the growth process that began with flowering and continued through the stages of nut development.
During this time, pistachio trees have undergone significant changes from producing flowers to developing fruits. As a result, the nuts have reached their optimal size and flavor, making it suitable for harvesting.
Methods of Harvesting
The nuts are harvested using various methods, including shaking the tree or utilizing mechanical shakers to dislodge them from the branches. Shaking is an effective way to release ripe pistachios without damaging them. Mechanical shakers can efficiently remove a large quantity of nuts from multiple trees within a short period.
Careful handling during harvest is essential to preserve the quality of pistachios. Any damage incurred during this stage can affect both appearance and taste, ultimately impacting their market value.
It’s important to note that pistachio growers adhere to specific guidelines when harvesting in order to maintain high-quality standards throughout commercial production.
Preservation Techniques
After being harvested, pistachios undergo meticulous processing procedures such as hulling (removing outer husk) and drying before they become available for consumption. These practices contribute significantly towards maintaining product integrity while extending shelf life.
Pest management guidelines play a critical role in preserving crop quality post-harvest by preventing infestations from pests like navel orangeworms which can compromise nut quality if left unchecked.
Post-Harvest Processing of Pistachios
Hulling Process
Once the pistachios are harvested, they go through several processing steps to prepare them for consumption. Hulling is the first step in this process. The outer hulls of the pistachios need to be removed, and this is typically done using mechanical equipment. The machines crack open the hulls without damaging the nuts inside, ensuring that only the edible part is retained.
After being hulled, the pistachios move on to the next stage of post-harvest processing.
Drying and Sorting
Following hulling, drying plays a crucial role in preparing pistachios for consumption. Proper drying helps reduce moisture content in the nuts, which prevents mold growth and extends their shelf life. Once dried, sorting becomes essential to ensure that only high-quality nuts make it to market. During sorting, any remaining debris or imperfect nuts are removed from the batch.
The post-harvest stages significantly impact both quality and taste.
Pistachio growers must pay close attention to these post-harvest processes. Proper storage conditions play a vital role in maintaining freshness and flavor.
Challenges in Growing Pistachios
Pest Infestations
Pistachio growers face challenges from pest infestations such as aphids and mites. These pests can damage the trees and reduce nut production. To combat this, growers often implement integrated pest management strategies, including the use of beneficial insects to control harmful ones. For example, releasing ladybugs into pistachio orchards helps keep aphid populations in check without resorting to chemical pesticides.
Adverse Weather Conditions Adverse weather conditions, like frost or excessive heat, can significantly impact the health of pistachio trees and their ability to produce nuts. Frost during flowering season can lead to poor pollination and reduced yields. On the other hand, prolonged periods of extreme heat can cause stress on the trees, affecting both current crop yield and future tree health. Growers may employ techniques such as using wind machines for frost protection or installing micro-sprinklers for cooling during hot spells.
Disease Management
Ongoing disease management is crucial in pistachio cultivation due to potential threats from pathogens like Botryosphaeria panicle and shoot blight (BPSB). This disease affects blossoms and shoots, leading to reduced nut set and overall tree vigor if left unmanaged. To mitigate this risk, growers adopt preventive measures such as pruning infected branches promptly after harvest and applying fungicides at specific times during the growing season.
Irrigation Efficiency Irrigation efficiency represents a continuous challenge for pistachio growers because inadequate water supply can affect tree growth and productivity while excess irrigation may lead to salt accumulation in soil. Drip irrigation systems are commonly used by farmers since they provide precise water delivery directly to the root zone while minimizing evaporation loss compared to traditional flood irrigation methods.
Environmental Impact of Pistachio Cultivation
Sustainable Farming Practices
Pistachio cultivation can have a significant environmental impact. However, sustainable farming practices are crucial in mitigating these effects. For instance, water conservation is essential in regions where pistachios are grown, as water scarcity is a common issue. By employing drip irrigation systems and other efficient watering techniques, farmers can reduce water usage while still ensuring the healthy growth of pistachio trees.
Efficient use of resources such as energy and fertilizers also plays a vital role in sustainable pistachio cultivation. Farmers can utilize renewable energy sources to power their operations, reducing reliance on non-renewable energy and lowering carbon emissions. By carefully managing fertilizer application through precision agriculture methods, they can minimize nutrient runoff into surrounding ecosystems.
Conserving soil health through practices like cover cropping and minimal tillage is another important aspect of sustainable pistachio cultivation. These methods help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil fertility over the long term.
Biodiversity Conservation Efforts
Within pistachio orchards, biodiversity conservation efforts contribute to overall environmental health. By planting native vegetation around orchard borders or within the orchards themselves, farmers create habitats for beneficial insects and wildlife species that contribute to pest control and pollination. This approach reduces the need for chemical pesticides while promoting natural ecological balance within the farming environment.
Furthermore, maintaining hedgerows or wooded areas within or near pistachio orchards provides nesting sites for birds that play an essential role in insect population regulation. This integrated pest management strategy helps control harmful pests without relying solely on chemical interventions.
Final Remarks
Congratulations! You’ve now gained a deep understanding of how pistachios grow, from the intricate life cycle of the pistachio tree to the challenges and environmental impact of its cultivation. As you delve into the world of pistachio farming, remember that optimal growing conditions and careful post-harvest processing are crucial for producing those delectable, nutrient-packed nuts we all love.
Now that you’re armed with this knowledge, why not consider supporting sustainable pistachio farming practices? Whether it’s choosing responsibly sourced pistachios or spreading awareness about eco-friendly cultivation methods, your actions can make a real difference. So, go ahead and share your newfound insights with friends and family – together, we can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future for pistachio cultivation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do pistachios grow?
Pistachios grow on trees in clusters, similar to grapes. The tree goes through a yearly cycle of blossoming, pollination, and nut development. Ideal growing conditions include well-drained soil and long, hot summers with low humidity.
What is the pollination process for pistachio cultivation?
Pistachio trees are dioecious, meaning some trees bear only male flowers while others produce only female flowers. Pollination occurs primarily by wind. It’s crucial to have a good ratio of male to female trees to ensure successful nut production.
When are pistachios harvested?
Pistachios are typically harvested in late August through early October when the hulls split open. This is known as dehiscence and indicates that the nuts are ripe for harvest. Harvesting involves shaking the tree limbs or using machines to collect the fallen nuts.
What are some challenges in growing pistachios?
Challenges in pistachio cultivation can include susceptibility to certain diseases such as Botryosphaeria blight and pests like navel orangeworms. Managing water usage efficiently is essential due to increasing concerns about water scarcity in many regions where pistachios are grown.
What is the environmental impact of pistachio cultivation?
Pistachio cultivation can have positive environmental impacts when managed sustainably but may also pose challenges related to water use and land management practices. Sustainable farming methods such as efficient irrigation systems and integrated pest management help minimize negative effects on the environment.